客户端
Pydantic AI 可以作为 MCP 客户端,连接到 MCP 服务器以使用其工具。
安装
您需要安装 pydantic-ai,或者带有 mcp 可选组的 pydantic-ai-slim。
pip install "pydantic-ai-slim[mcp]"
uv add "pydantic-ai-slim[mcp]"
用法
Pydantic AI 提供了两种连接 MCP 服务器的方式:
MCPServerStreamableHTTP:使用 可流式 HTTP 传输协议连接到 MCP 服务器。MCPServerSSE:使用 HTTP SSE 传输协议连接到 MCP 服务器。MCPServerStdio:将服务器作为子进程运行,并使用 stdio 传输协议与其连接。
下面展示了这三种方式的示例。
每个 MCP 服务器实例都是一个工具集,可以使用 toolsets 参数注册到 Agent 中。
您可以使用 async with agent 上下文管理器,在代理运行将使用服务器的上下文中,打开和关闭所有已注册服务器的连接(对于 stdio 服务器,则是启动和停止子进程)。您也可以使用 async with server 来管理特定服务器的连接或子进程,例如,当您想在多个代理中使用它时。如果您没有显式地进入这些上下文管理器来设置服务器,它会在需要时自动完成(例如,在列出可用工具或调用特定工具时),但在您期望使用服务器的整个上下文中进行设置会更高效。
可流式 HTTP 客户端
MCPServerStreamableHTTP 通过 HTTP 使用 可流式 HTTP 传输协议连接到服务器。
注意
MCPServerStreamableHTTP 要求在运行代理之前,有一个正在运行并接受 HTTP 连接的 MCP 服务器。Pydantic AI 不负责管理服务器的运行。
在创建可流式 HTTP 客户端之前,我们需要运行一个支持可流式 HTTP 传输协议的服务器。
from mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCP
app = FastMCP()
@app.tool()
def add(a: int, b: int) -> int:
return a + b
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(transport='streamable-http')
然后我们可以创建客户端。
from pydantic_ai import Agent
from pydantic_ai.mcp import MCPServerStreamableHTTP
server = MCPServerStreamableHTTP('https://:8000/mcp') # (1)!
agent = Agent('openai:gpt-4o', toolsets=[server]) # (2)!
async def main():
async with agent: # (3)!
result = await agent.run('What is 7 plus 5?')
print(result.output)
#> The answer is 12.
- 使用连接 URL 定义 MCP 服务器。
- 创建一个附加了 MCP 服务器的代理。
- 创建一个客户端会话以连接到服务器。
(此示例是完整的,可以“按原样”运行——您需要添加 asyncio.run(main()) 来运行 main)
这里发生了什么?
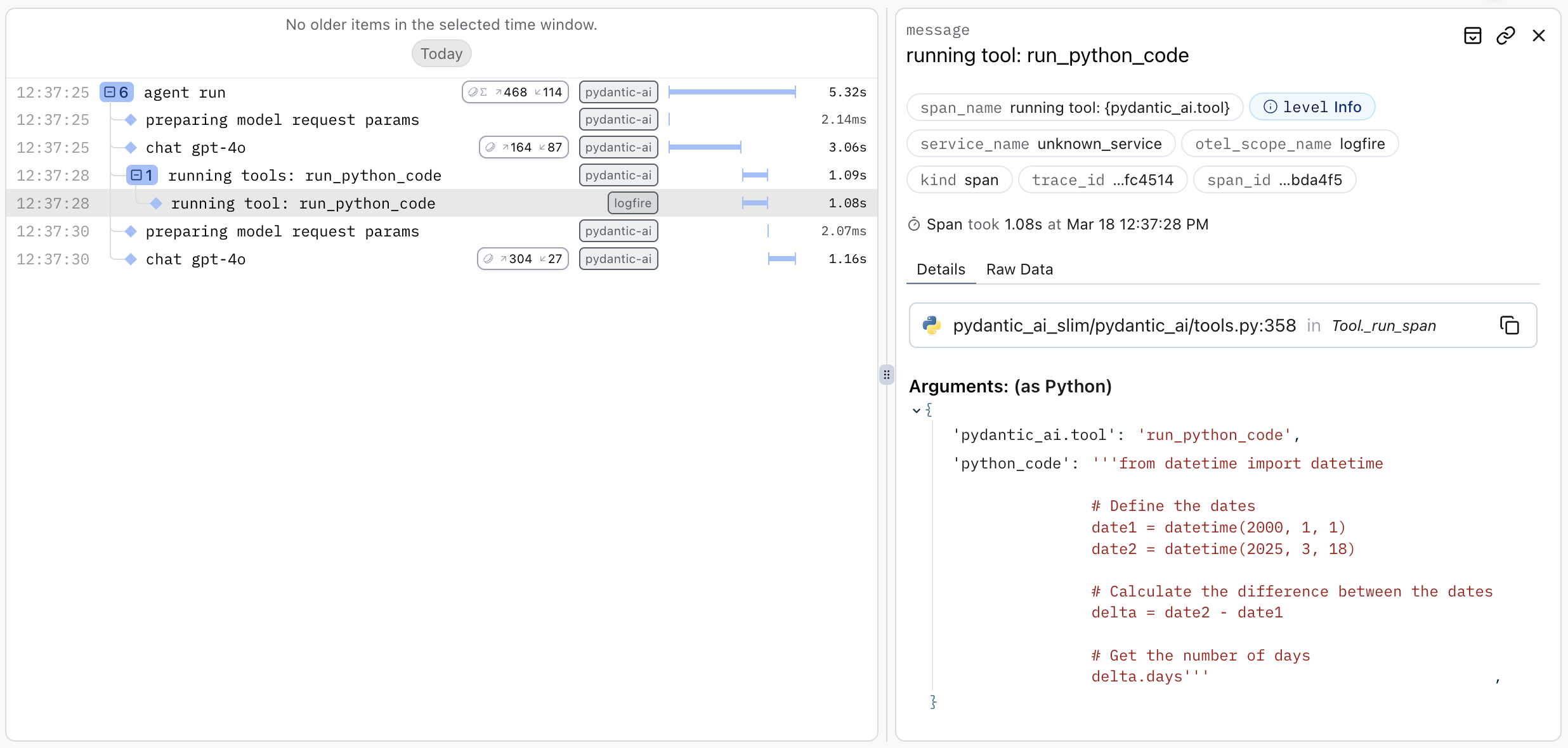
- 模型收到了提示:“2000-01-01 和 2025-03-18 之间相隔多少天?”
- 模型决定:“哦,我有一个
run_python_code工具,这会是回答这个问题的好方法”,然后编写了一些 Python 代码来计算答案。 - 模型返回一个工具调用。
- Pydantic AI 使用 SSE 传输协议将工具调用发送到 MCP 服务器。
- 模型再次被调用,并传入运行代码的返回值。
- 模型返回最终答案。
您可以通过添加三行代码,使用 logfire 来检测这个例子,从而清晰地将这个过程可视化,甚至可以看到运行的代码。
import logfire
logfire.configure()
logfire.instrument_pydantic_ai()
将显示如下内容:
SSE 客户端
MCPServerSSE 通过 HTTP 使用 HTTP + 服务器发送事件 (SSE) 传输协议连接到服务器。
注意
MCP 中的 SSE 传输协议已被弃用,您应改用可流式 HTTP。
在创建 SSE 客户端之前,我们需要运行一个支持 SSE 传输协议的服务器。
from mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCP
app = FastMCP()
@app.tool()
def add(a: int, b: int) -> int:
return a + b
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(transport='sse')
然后我们可以创建客户端。
from pydantic_ai import Agent
from pydantic_ai.mcp import MCPServerSSE
server = MCPServerSSE('https://:3001/sse') # (1)!
agent = Agent('openai:gpt-4o', toolsets=[server]) # (2)!
async def main():
async with agent: # (3)!
result = await agent.run('What is 7 plus 5?')
print(result.output)
#> The answer is 12.
- 使用连接 URL 定义 MCP 服务器。
- 创建一个附加了 MCP 服务器的代理。
- 创建一个客户端会话以连接到服务器。
(此示例是完整的,可以“按原样”运行——您需要添加 asyncio.run(main()) 来运行 main)
MCP "stdio" 服务器
MCP 还提供了 stdio 传输协议,其中服务器作为子进程运行,并通过 stdin 和 stdout 与客户端通信。在这种情况下,您将使用 MCPServerStdio 类。
在这个例子中,mcp-run-python 被用作 MCP 服务器。
from pydantic_ai import Agent
from pydantic_ai.mcp import MCPServerStdio
server = MCPServerStdio( # (1)!
'uv', args=['run', 'mcp-run-python', 'stdio'], timeout=10
)
agent = Agent('openai:gpt-4o', toolsets=[server])
async def main():
async with agent:
result = await agent.run('How many days between 2000-01-01 and 2025-03-18?')
print(result.output)
#> There are 9,208 days between January 1, 2000, and March 18, 2025.
- 有关更多信息,请参阅 MCP Run Python。
工具调用自定义
MCP 服务器提供了设置 process_tool_call 的功能,这允许自定义工具调用请求及其响应。
一个常见的用例是向服务器调用所需的请求中注入元数据。
from typing import Any
from pydantic_ai import Agent, RunContext
from pydantic_ai.mcp import CallToolFunc, MCPServerStdio, ToolResult
from pydantic_ai.models.test import TestModel
async def process_tool_call(
ctx: RunContext[int],
call_tool: CallToolFunc,
name: str,
tool_args: dict[str, Any],
) -> ToolResult:
"""A tool call processor that passes along the deps."""
return await call_tool(name, tool_args, {'deps': ctx.deps})
server = MCPServerStdio('python', args=['mcp_server.py'], process_tool_call=process_tool_call)
agent = Agent(
model=TestModel(call_tools=['echo_deps']),
deps_type=int,
toolsets=[server]
)
async def main():
async with agent:
result = await agent.run('Echo with deps set to 42', deps=42)
print(result.output)
#> {"echo_deps":{"echo":"This is an echo message","deps":42}}
使用工具前缀避免命名冲突
当连接到多个可能提供同名工具的 MCP 服务器时,您可以使用 tool_prefix 参数来避免命名冲突。此参数会为来自特定服务器的所有工具名称添加一个前缀。
这使您可以使用多个可能具有重叠工具名称的服务器而不会发生冲突。
from pydantic_ai import Agent
from pydantic_ai.mcp import MCPServerSSE
# Create two servers with different prefixes
weather_server = MCPServerSSE(
'https://:3001/sse',
tool_prefix='weather' # Tools will be prefixed with 'weather_'
)
calculator_server = MCPServerSSE(
'https://:3002/sse',
tool_prefix='calc' # Tools will be prefixed with 'calc_'
)
# Both servers might have a tool named 'get_data', but they'll be exposed as:
# - 'weather_get_data'
# - 'calc_get_data'
agent = Agent('openai:gpt-4o', toolsets=[weather_server, calculator_server])
自定义 TLS / SSL 配置
在某些环境中,您需要调整 HTTPS 连接的建立方式——例如,信任内部的证书颁发机构(CA),为 mTLS 提供客户端证书,或者(仅在本地开发时!)完全禁用证书验证。所有基于 HTTP 的 MCP 客户端类(MCPServerStreamableHTTP 和 MCPServerSSE)都公开了一个 http_client 参数,允许您传入自己预先配置的 httpx.AsyncClient。
import ssl
import httpx
from pydantic_ai import Agent
from pydantic_ai.mcp import MCPServerSSE
# Trust an internal / self-signed CA
ssl_ctx = ssl.create_default_context(cafile='/etc/ssl/private/my_company_ca.pem')
# OPTIONAL: if the server requires **mutual TLS** load your client certificate
ssl_ctx.load_cert_chain(certfile='/etc/ssl/certs/client.crt', keyfile='/etc/ssl/private/client.key',)
http_client = httpx.AsyncClient(
verify=ssl_ctx,
timeout=httpx.Timeout(10.0),
)
server = MCPServerSSE(
'https://:3001/sse',
http_client=http_client, # (1)!
)
agent = Agent('openai:gpt-4o', toolsets=[server])
async def main():
async with agent:
result = await agent.run('How many days between 2000-01-01 and 2025-03-18?')
print(result.output)
#> There are 9,208 days between January 1, 2000, and March 18, 2025.
- 当您提供
http_client时,Pydantic AI 会为每个请求重用此客户端。因此,httpx 支持的任何配置(verify、cert、自定义代理、超时等)都将应用于所有 MCP 流量。
MCP 采样
什么是 MCP 采样 (Sampling)?
在 MCP 中,采样是一个系统,MCP 服务器可以通过 MCP 客户端进行 LLM 调用——实际上是通过客户端,使用任何正在使用的传输协议,将请求代理到 LLM。
当 MCP 服务器需要使用生成式 AI,但您不想为每个服务器都配置自己的 LLM 凭证,或者当一个公共 MCP 服务器希望连接的客户端来支付 LLM 调用费用时,采样功能非常有用。
令人困惑的是,这个概念与可观测性中的“采样”概念无关,坦率地说,也与任何其他领域中的“采样”概念无关。
采样图
这是一个 Mermaid 图,它或许能让数据流更清晰一些。
sequenceDiagram
participant LLM
participant MCP_Client as MCP client
participant MCP_Server as MCP server
MCP_Client->>LLM: LLM call
LLM->>MCP_Client: LLM tool call response
MCP_Client->>MCP_Server: tool call
MCP_Server->>MCP_Client: sampling "create message"
MCP_Client->>LLM: LLM call
LLM->>MCP_Client: LLM text response
MCP_Client->>MCP_Server: sampling response
MCP_Server->>MCP_Client: tool call responsePydantic AI 作为客户端和服务器都支持采样。有关如何在服务器中使用采样的详细信息,请参阅服务器文档。
当 Pydantic AI 代理作为客户端时,会自动支持采样。
为了能够使用采样,MCP 服务器实例需要设置一个 sampling_model。这可以直接在服务器上通过构造函数关键字参数或属性来完成,也可以通过使用 agent.set_mcp_sampling_model() 将代理的模型或指定为参数的模型设置为该代理注册的所有 MCP 服务器的采样模型。
假设我们有一个想要使用采样的 MCP 服务器(在本例中,是根据工具参数生成一个 SVG)。
采样 MCP 服务器
import re
from pathlib import Path
from mcp import SamplingMessage
from mcp.server.fastmcp import Context, FastMCP
from mcp.types import TextContent
app = FastMCP()
@app.tool()
async def image_generator(ctx: Context, subject: str, style: str) -> str:
prompt = f'{subject=} {style=}'
# `ctx.session.create_message` is the sampling call
result = await ctx.session.create_message(
[SamplingMessage(role='user', content=TextContent(type='text', text=prompt))],
max_tokens=1_024,
system_prompt='Generate an SVG image as per the user input',
)
assert isinstance(result.content, TextContent)
path = Path(f'{subject}_{style}.svg')
# remove triple backticks if the svg was returned within markdown
if m := re.search(r'^```\w*$(.+?)```$', result.content.text, re.S | re.M):
path.write_text(m.group(1))
else:
path.write_text(result.content.text)
return f'See {path}'
if __name__ == '__main__':
# run the server via stdio
app.run()
在 Agent 中使用此服务器将自动允许采样。
from pydantic_ai import Agent
from pydantic_ai.mcp import MCPServerStdio
server = MCPServerStdio('python', args=['generate_svg.py'])
agent = Agent('openai:gpt-4o', toolsets=[server])
async def main():
async with agent:
agent.set_mcp_sampling_model()
result = await agent.run('Create an image of a robot in a punk style.')
print(result.output)
#> Image file written to robot_punk.svg.
(这个例子是完整的,可以“按原样”运行)
您可以通过在创建服务器引用时设置 allow_sampling=False 来禁止采样,例如:
from pydantic_ai.mcp import MCPServerStdio
server = MCPServerStdio(
'python',
args=['generate_svg.py'],
allow_sampling=False,
)
信息诱导 (Elicitation)
在 MCP 中,信息诱导 (elicitation) 允许服务器在会话期间,当缺少或需要额外上下文时,向客户端请求结构化输入。
信息诱导让模型基本上可以说:“等等——在我继续之前,我需要知道 X”,而不是要求一次性提供所有信息或凭空猜测。
信息诱导 (Elicitation) 的工作原理
信息诱导引入了一种新的协议消息类型,称为 ElicitRequest,当服务器需要额外信息时,它会从服务器发送到客户端。然后,客户端可以响应一个 ElicitResult 或一个 ErrorData 消息。
这是一个典型的交互过程:
- 用户向 MCP 服务器发出请求(例如,“在那家意大利餐厅订个位子”)。
- 服务器识别出它需要更多信息(例如,“哪家意大利餐厅?”,“什么日期和时间?”)。
- 服务器向客户端发送一个
ElicitRequest,请求缺失的信息。 - 客户端接收到请求,并将其呈现给用户(例如,通过终端提示、GUI 对话框或 Web 界面)。
- 用户提供所请求的信息,或者选择
拒绝 (decline)或取消 (cancel)请求。 - 客户端将带有用户响应的
ElicitResult发送回服务器。 - 有了这些结构化数据,服务器就可以继续处理原始请求。
这允许了更具交互性和用户友好的体验,尤其适用于多阶段工作流。服务器不需要预先获取所有信息,而是在需要时进行询问,使交互感觉更自然。
设置信息诱导 (Elicitation)
要启用信息诱导,请在创建 MCP 服务器实例时提供一个 elicitation_callback 函数。
from mcp.server.fastmcp import Context, FastMCP
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
mcp = FastMCP(name='Restaurant Booking')
class BookingDetails(BaseModel):
"""Schema for restaurant booking information."""
restaurant: str = Field(description='Choose a restaurant')
party_size: int = Field(description='Number of people', ge=1, le=8)
date: str = Field(description='Reservation date (DD-MM-YYYY)')
@mcp.tool()
async def book_table(ctx: Context) -> str:
"""Book a restaurant table with user input."""
# Ask user for booking details using Pydantic schema
result = await ctx.elicit(message='Please provide your booking details:', schema=BookingDetails)
if result.action == 'accept' and result.data:
booking = result.data
return f'✅ Booked table for {booking.party_size} at {booking.restaurant} on {booking.date}'
elif result.action == 'decline':
return 'No problem! Maybe another time.'
else: # cancel
return 'Booking cancelled.'
if __name__ == '__main__':
mcp.run(transport='stdio')
此服务器通过在调用 book_table 工具时向客户端请求结构化的预订详细信息来演示信息诱导。以下是如何创建一个处理这些信息诱导请求的客户端:
import asyncio
from typing import Any
from mcp.client.session import ClientSession
from mcp.shared.context import RequestContext
from mcp.types import ElicitRequestParams, ElicitResult
from pydantic_ai import Agent
from pydantic_ai.mcp import MCPServerStdio
async def handle_elicitation(
context: RequestContext[ClientSession, Any, Any],
params: ElicitRequestParams,
) -> ElicitResult:
"""Handle elicitation requests from MCP server."""
print(f'\n{params.message}')
if not params.requestedSchema:
response = input('Response: ')
return ElicitResult(action='accept', content={'response': response})
# Collect data for each field
properties = params.requestedSchema['properties']
data = {}
for field, info in properties.items():
description = info.get('description', field)
value = input(f'{description}: ')
# Convert to proper type based on JSON schema
if info.get('type') == 'integer':
data[field] = int(value)
else:
data[field] = value
# Confirm
confirm = input('\nConfirm booking? (y/n/c): ').lower()
if confirm == 'y':
print('Booking details:', data)
return ElicitResult(action='accept', content=data)
elif confirm == 'n':
return ElicitResult(action='decline')
else:
return ElicitResult(action='cancel')
# Set up MCP server connection
restaurant_server = MCPServerStdio(
'python', args=['restaurant_server.py'], elicitation_callback=handle_elicitation
)
# Create agent
agent = Agent('openai:gpt-4o', toolsets=[restaurant_server])
async def main():
"""Run the agent to book a restaurant table."""
async with agent:
result = await agent.run('Book me a table')
print(f'\nResult: {result.output}')
if __name__ == '__main__':
asyncio.run(main())
支持的模式类型 (Schema Types)
MCP 信息诱导仅支持字符串、数字、布尔和枚举类型,且仅支持扁平对象结构。这些限制确保了跨客户端的可靠兼容性。详情请参阅支持的模式类型。
安全性
MCP 信息诱导需要谨慎处理——服务器不得请求敏感信息,客户端必须实施带有明确解释的用户批准控制。详情请参阅安全注意事项。